Inside China’s AI Hospital Town: The Virtual Future of Medicine Is Here
China’s AI hospital town, built by Tsinghua University, simulates an entire healthcare system using LLMs—redefining diagnostics, medical training, and public health with global implications.
China has taken a bold leap into the future of medicine with the creation of the world’s first AI hospital town. Developed by researchers at Tsinghua University, this pioneering initiative fuses large language models (LLMs), virtual patient simulation, and digital twin technology to reimagine how healthcare is delivered, learned, and scaled. The Agent Hospital isn't just a showcase of cutting-edge artificial intelligence—it's a living laboratory that may reshape global medical education, diagnostics, and public health planning.
A Fully Simulated Healthcare Ecosystem
At the heart of China’s AI hospital town is a network of intelligent agents—AI doctors, nurses, administrators, and patients—all powered by LLMs capable of continuous autonomous interaction and learning. Unlike conventional digital health platforms that focus on specific services, this virtual town replicates an entire healthcare environment.
The AI doctors in the Agent Hospital autonomously consult, diagnose, and treat virtual patients with a diagnostic accuracy of up to 93.06% on the MedQA dataset. More than just software, these agents learn from each interaction, improving over time like real-world clinicians.
Breakthroughs in Virtual Medical Training and Simulation
One of the most compelling applications of this virtual ecosystem lies in its capacity for immersive simulation. The AI hospital town serves as a training ground for both AI systems and medical students. Virtual patients, complete with realistic symptoms and physiological responses, allow trainees to observe, diagnose, and treat in risk-free environments.
This innovation makes it possible to treat 10,000 cases in just days—a task that would take human doctors over two years. The simulations extend to public health crises, such as infectious disease outbreaks, enabling predictive modeling and strategy testing without endangering real populations.
"The system can simulate and predict various medical scenarios, such as the spread, development and control of infectious diseases in a region," says Liu Yang, project leader of the Agent Hospital.
The Tech Stack Powering the Revolution
The Agent Hospital's core is a powerful technological framework that brings together LLMs, computer vision, machine learning, and digital twins.
- LLMs analyze patient data, interpret medical language, and enable human-like interaction.
- Computer vision tools interpret X-rays, CT scans, and pathological images.
- Digital twins create real-time replicas of hospital operations, facilities, and even patients.
- Predictive analytics help optimize staffing, resource allocation, and care outcomes.
These technologies are integrated to simulate the entire continuum of care, from triage to discharge, while continuously refining clinical protocols and system operations.
How Accurate Are AI Doctors?
The accuracy and reliability of AI in healthcare have seen remarkable gains. While general LLMs show variable performance, more specialized systems are achieving results that rival human doctors.

These figures highlight how AI, when properly trained and deployed, can function as a powerful clinical decision support system—particularly when paired with human oversight.
Companies Leading the AI Healthcare Revolution
As AI healthcare tools move from pilot projects to mainstream adoption, several companies are at the forefront of innovation and deployment:
- IBM Watson Health (now Merative): One of the early pioneers in AI healthcare applications, focusing on cancer diagnostics, clinical decision support, and health data analytics.
- Google DeepMind: Known for its work in medical imaging, DeepMind developed AI tools that outperform radiologists in diagnosing eye diseases and breast cancer.
- NVIDIA: Beyond GPUs, NVIDIA powers AI medical imaging and research through its Clara platform, used by hospitals and startups globally.
- Microsoft + Nuance: Through its acquisition of Nuance, Microsoft has embedded AI into clinical documentation, ambient intelligence, and virtual care tools.
- Tempus: A leader in AI-driven precision medicine and oncology, combining clinical and molecular data for personalized treatment plans.
- Ping An Good Doctor (China): One of the largest AI health platforms in China, offering virtual consultations, diagnostics, and pharmacy services.
- Babylon Health: A U.K.-based firm providing AI-powered health assessments and telehealth, with growing global reach.
These players are shaping the infrastructure and accessibility of AI-driven healthcare worldwide, often working in tandem with hospitals, academic institutions, and governments.
Transformative Potential and Ethical Crossroads
Beyond diagnostic efficiency, the AI hospital town offers a glimpse into the future of global healthcare equity. With AI-powered mobile clinics and telemedicine platforms, specialist-level care could reach remote or underserved areas. Automating administrative workflows, optimizing patient flow, and reducing readmissions by 15–20% also promises significant cost savings.
Yet, the path forward is not without friction. Ethical and regulatory challenges loom large:
- Algorithmic bias from non-diverse training data
- Privacy and consent across jurisdictions
- Cultural acceptance of AI in healthcare
Experts caution that AI can support but not replace the irreplaceable human elements of empathy, ethics, and emotional intelligence.
Comparing Regional Adoption and Investment
AI healthcare adoption rates vary globally, shaped by funding, regulation, and public health needs. Here’s a snapshot of adoption metrics across regions:
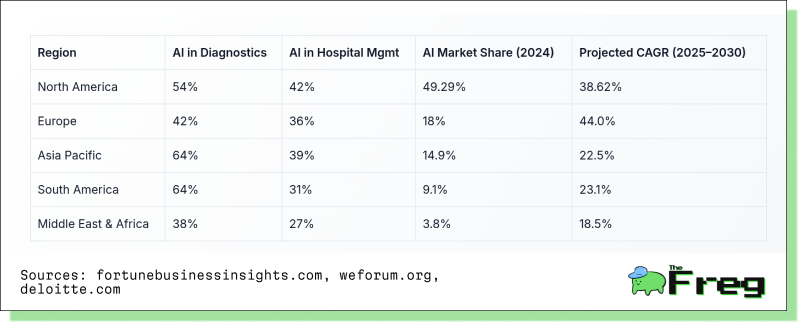
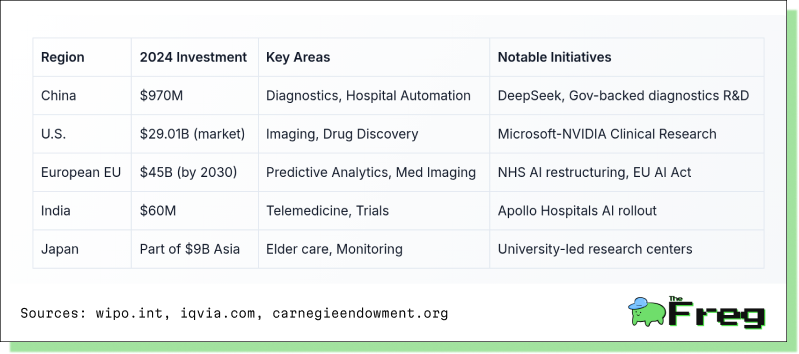
Meanwhile, global healthcare AI investment is surging, led by China and the U.S.
Regulation: China vs the West
China's regulatory framework encourages rapid innovation with centralized oversight and strategic alignment. This model enables swift deployment of systems like the Agent Hospital. In contrast, Western systems such as the U.K.'s NHS and the U.S. FDA emphasize privacy, safety, and ethics, often resulting in slower implementation timelines.
For example, the U.K.-based Babylon Health, which developed an AI health app with 80% diagnostic accuracy, had to navigate complex national health regulations despite raising over $550 million in funding.
Augmentation, Not Replacement
Looking forward, AI hospital towns will likely evolve into hybrid systems where virtual care complements physical facilities. AI will serve as a force multiplier for healthcare workers, taking over routine tasks, optimizing workflows, and providing decision support, all while enabling personalized, adaptive medical training.
But the promise of AI cannot be realized without ethical foresight. From ensuring equitable access to protecting data privacy, the future of AI in medicine hinges on a balance between innovation and compassion. China’s AI hospital town may be the first of its kind, but its real success will depend on how responsibly the world follows its lead.