India's Steel Sector: Navigating Global Headwinds with Domestic Resilience
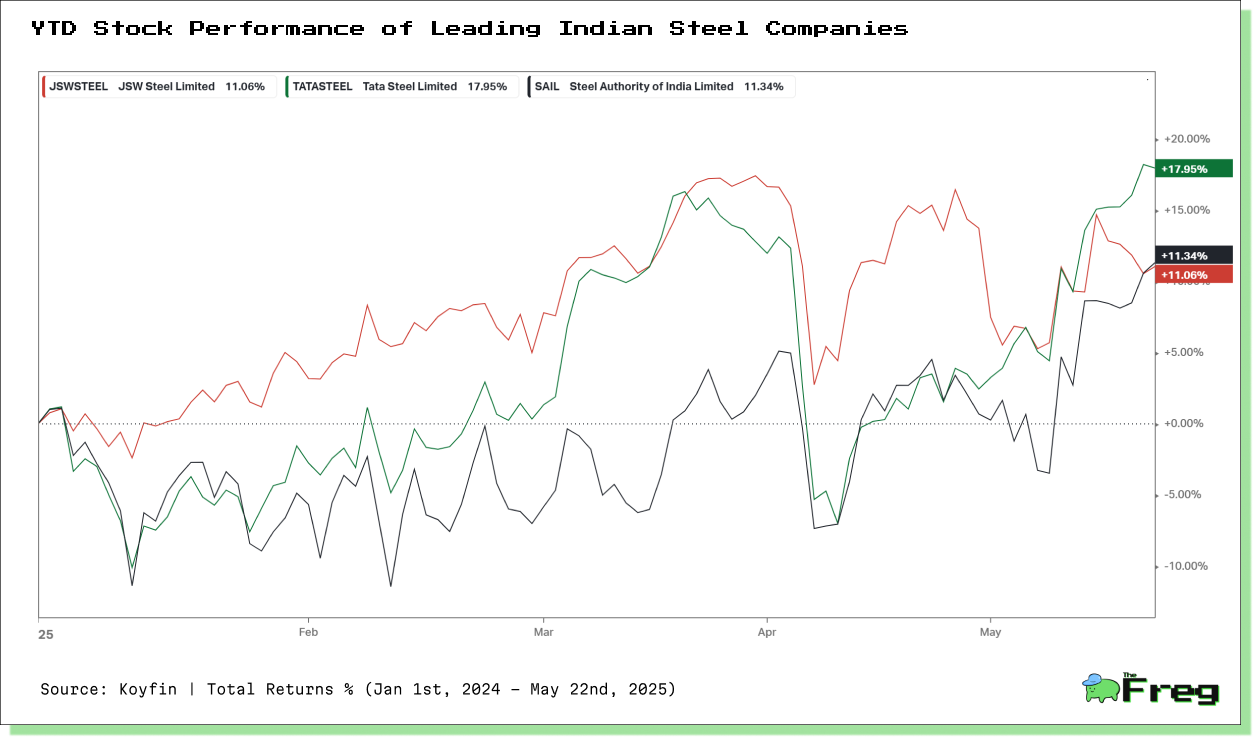
A data-driven comparison of Tata Steel, JSW Steel, and SAIL's stock performance, highlighting key trends, investor sentiment, and market forces shaping India's steel sector between 2024 and 2025.

India's steel industry is poised for significant growth in 2025, with domestic demand projected to rise by 8-9%, according to CRISIL. This robust outlook contrasts sharply with the global steel demand, which declined by approximately 1% in 2024, highlighting India's unique position in the global steel landscape.
Domestic Demand: A Beacon Amid Global Slump
While major economies like China, the US, and Europe experienced contractions in steel demand in 2024, India bucked the trend with an 11% increase. This surge is attributed to the government's aggressive infrastructure initiatives, including Bharatmala, Sagarmala, and the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY), which have significantly boosted steel consumption in construction and related sectors.
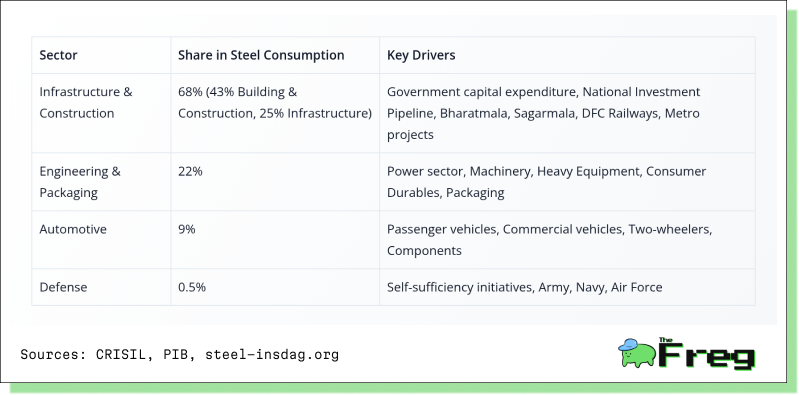
The following table illustrates the sector-wise steel consumption in India:
Safeguard Duty: Shielding Domestic Producers
In response to the surge in low-cost steel imports, primarily from China, Japan, and Vietnam, India imposed a 12% safeguard duty on specific steel products for 200 days. This measure aims to protect domestic manufacturers from excessive imports, especially as India became a net importer of finished steel for the second consecutive year in 2024/25, with imports reaching a nine-year high of 9.5 million metric tons.
The immediate impact of this duty includes:
- An approximate increase of $71 per ton in import costs, providing a pricing cushion for domestic producers.
- A rise in domestic steel prices by ₹1,700 per ton in anticipation of the duty.
- Potential price hikes by steel manufacturers of ₹2,000-2,500 per ton, boosting their margins.
However, downstream industries like automotive, infrastructure, and renewable energy may face higher input costs, and critics argue that the duty could raise costs for manufacturers dependent on imported materials.
Raw Material Dynamics: Coking Coal Prices in Flux
Coking coal, a critical input for steel production, is projected to average $220 per ton in 2025, according to BMI, a Fitch Solutions company. This forecast comes despite a downward trend in prices, ending 2024 at $200 per ton.
Several factors influence this outlook:
- Australian production disruptions from heavy rainfall in Queensland boosted prices in early 2024.
- China's weakening property sector and reduced steel production created downward pressure throughout most of the year.
- Long-term downward pressure is expected as global blast furnace steel production slows amid the green economy transition.
For Indian steel producers, the decline in coking coal prices offers some relief, especially for those reliant on imports. However, the benefits are uneven, with vertically integrated producers like Tata Steel, which have captive iron ore mines, better positioned to weather input cost volatility.
Tata Steel: Leveraging Domestic Strength
Tata Steel has strategically positioned itself to capitalize on India's robust steel demand growth. In FY2025, the company achieved record domestic production of 21.8 million tons, a 5% year-on-year increase. This growth was powered by the commissioning of India's largest blast furnace at Kalinganagar and enhanced production at Neelachal Ispat Nigam Limited.
Key strategic advantages for Tata Steel include:
- Achieving nearly 100% capacity utilization across existing plants, maximizing economies of scale.
- Becoming the first Indian mill to localize high-strength grade hot-rolled CP780 for automotive applications.
- Maintaining leadership in the automotive sector with Tata Tiscon achieving "best ever" volumes, growing 19% year-on-year to 2.4 million tons.
- Expanding into new segments, including commercial shipbuilding, while investing over ₹1,600 crores in R&D over five years.
- Mining approximately 40 million tons of iron ore across its Indian operations, supporting vertical integration.
Global Export Landscape: China's Shifting Role
China's steel exports reached an all-time high of 110.72 million tons in 2024, up 22.7% from 2023, despite domestic steel production falling by 1.7% to a five-year low of 1.005 billion tons.
However, these record exports are proving unsustainable as global trade barriers mount rapidly. Rising trade barriers, including 124 anti-dumping policies implemented against Chinese steel since 2024, and tariffs imposed by key markets like the US, South Korea, and Vietnam, are expected to reduce China's steel exports by up to 20% in the second quarter compared to Q1 levels.
This export slowdown creates a strategic opportunity for Indian steel producers to capture market share in regions like the Middle East, Africa, and South America while benefiting from reduced pricing pressure in domestic markets.
Valuation Metrics: Assessing Investment Opportunities
The following table presents key valuation metrics for India's top steel producers, highlighting their current market positioning relative to historical averages:
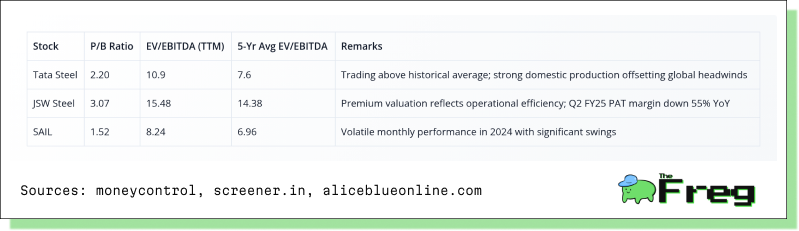
These valuations reflect investors' cautious optimism about India's steel sector despite global challenges. Tata Steel's EV/EBITDA ratio has increased significantly from its five-year average, indicating higher investor expectations based on its domestic market strength and vertical integration advantages. JSW Steel maintains premium multiples despite recent earnings pressure, while SAIL offers a relatively lower valuation with higher volatility in stock performance.
Strategic Outlook: Balancing Opportunities and Risks
India's steel sector demonstrates remarkable resilience amid global volatility, with domestic demand projected to grow by 8-9% in 2025, significantly outpacing global markets. This growth is primarily driven by infrastructure development, construction activities, and rising demand from engineering and packaging industries. The government's ambitious infrastructure projects and Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, which has approved 12 new steel plants, provide strong foundational support for sustained demand.
Investors should maintain a domestic-focused strategy while closely monitoring external risks. Companies with vertical integration advantages, like captive iron ore mines, are better positioned to weather input cost volatility. The sector benefits from improving raw material dynamics, with coking coal prices declining by 18% year-on-year to approximately $270 per ton and domestic iron ore prices reduced by 12% from 2023 peaks. However, caution is warranted as global economic uncertainties, Chinese export pressures, and potential margin compression from rising imports remain significant challenges. The most resilient investment opportunities lie with producers demonstrating cost leadership, operational efficiency, and healthy balance sheets that can navigate both domestic opportunities and international headwinds.